Securing Your Active Directory-Based File-Sharing System: A Comprehensive Audit and Risk Assessment
I’m learning how to create effective audits and security assessments for Active Directory-based file-sharing systems. In this blog, I explore how to identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and enhance security with tools like Wazuh

Introduction
As part of my journey in mastering effective auditing and security assessments, I’m diving into securing Active Directory-based file-sharing systems. In this blog, I share what I’ve learned about identifying vulnerabilities, such as inactive user accounts and weak passwords, and how to implement strategies for risk mitigation. I also explore how integrating security tools like Wazuh for real-time monitoring and log analysis can elevate the security of these systems. This guide is a helpful resource for anyone looking to improve their system's security and audit practices.
Active Directory File-Sharing System Audit and Risk Assessment
Scenario
A company wants to assess the security of its internal Active Directory-based file-sharing system due to concerns about unauthorized access.
Task
Conduct an audit and identify risks associated with the Active Directory file-sharing system.
Steps and Findings
Scope
Audit the Active Directory file-sharing system to evaluate access controls, user permissions, and overall system configuration to identify vulnerabilities.
Data Collection
- Reviewed the Active Directory user access list and permission settings.
- Analyzed system logs for the past 30 days for unusual activity.
- Conducted a security scan of Active Directory groups, organizational units, and user roles.
- Checked group policies and password policies configured within Active Directory.
- Reviewed the file-sharing server’s configuration related to Active Directory integration.
- Integrated Wazuh to enhance log analysis, real-time monitoring, and vulnerability detection.
Findings
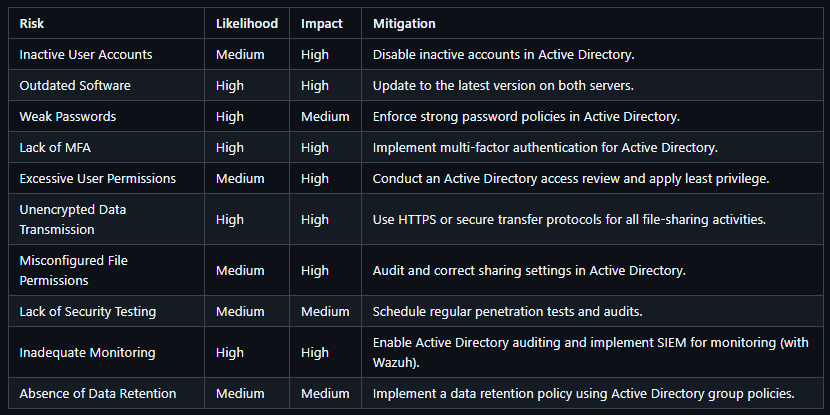
Vulnerability 1: Inactive User Accounts
- Issue: 15 user accounts have not been used in over 6 months.
- Risk: Possible misuse or compromise of inactive accounts.
- Recommendation: Disable or delete inactive accounts in Active Directory.
Vulnerability 2: Outdated Software
- Issue: The server is running an outdated software version (last updated 10 months ago).
- Risk: Susceptibility to known exploits.
- Recommendation: Apply the latest software updates and patches to both the file-sharing system and Active Directory server.
Vulnerability 3: Weak Passwords
- Issue: Weak passwords used by 10% of users (e.g., "123456", "password").
- Risk: High likelihood of brute-force attacks.
- Recommendation: Enforce a strong password policy via Active Directory, requiring users to have complex passwords.
Vulnerability 4: Lack of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Issue: MFA is not required for user access to the file-sharing system.
- Risk: Increased risk of unauthorized access if credentials are compromised.
- Recommendation: Implement MFA for Active Directory and related services to strengthen authentication security.
Vulnerability 5: Excessive User Permissions
- Issue: 20% of users have access to files outside their role's requirements.
- Risk: Potential for accidental or intentional data breaches.
- Recommendation: Conduct a review of Active Directory groups and permissions, applying the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to restrict access.
Vulnerability 6: Unencrypted Data Transmission
- Issue: Files are transmitted over the network without encryption (plain HTTP used).
- Risk: Interception of data during transmission (man-in-the-middle attacks).
- Recommendation: Enforce the use of HTTPS or secure file transfer protocols like SFTP for all file-sharing activities.
Vulnerability 7: Misconfigured Permissions on Shared Files
- Issue: 10% of files are set to "public" or shared with "everyone."
- Risk: Exposure of sensitive data to unauthorized individuals.
- Recommendation: Audit and correct file sharing permissions in Active Directory, ensuring access is granted only to authorized users.
Vulnerability 8: Lack of Regular Security Testing
- Issue: The system has not undergone penetration testing or security assessments in over a year.
- Risk: Undetected vulnerabilities may persist over time.
- Recommendation: Schedule regular security assessments and penetration tests, focusing on Active Directory configurations and permissions.
Vulnerability 9: Inadequate Monitoring and Alerting
- Issue: No real-time monitoring or alerts for unusual activities within Active Directory.
- Risk: Delayed detection of unauthorized access or system breaches.
- Recommendation: Implement Active Directory auditing and deploy a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for real-time monitoring and alerting using Wazuh for enhanced log analysis and threat detection.
Vulnerability 10: Absence of a Data Retention Policy
- Issue: Files that are no longer needed remain in the system indefinitely.
- Risk: Increased attack surface and exposure of outdated sensitive data.
- Recommendation: Implement a data retention policy for files, periodically archiving or deleting old files using Active Directory group policies.
Risk Assessment Table
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Mapping
The vulnerabilities and recommendations align with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), addressing core functions like Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Each vulnerability is mapped to NIST guidelines for a comprehensive risk management approach.
Integration with Wazuh
Wazuh is an open-source security monitoring platform that enhances the audit and risk assessment process by providing:
- Real-time monitoring and alerting for suspicious activities in Active Directory.
- Log analysis for detecting unusual patterns such as failed login attempts, privilege escalations, or unauthorized access to files.
- File integrity monitoring, ensuring files remain unchanged and secure.
- Vulnerability detection and compliance monitoring, ensuring systems comply with security standards.
By integrating Wazuh into your Active Directory monitoring system, you can:
- Achieve continuous auditing of user access, permissions, and activity.
- Respond quickly to security events with real-time alerts and incident management capabilities.
- Strengthen your organization's overall security posture by integrating Wazuh with other security tools such as SIEM for comprehensive threat detection.

